What is Addiction?
Addiction to drugs (opioids, alcohol, methamphetamine (meth), nicotine, marijuana, etc..), involves the participation of several brain circuits that evolved to sustain survival. There are 4 circuits in the brain that play a major role in addiction to drugs and in natural rewards, such as food, water, sex, and nurturing.²
What are the Major Brain Circuits?
The 4 major brain circuits in drug addiction are:
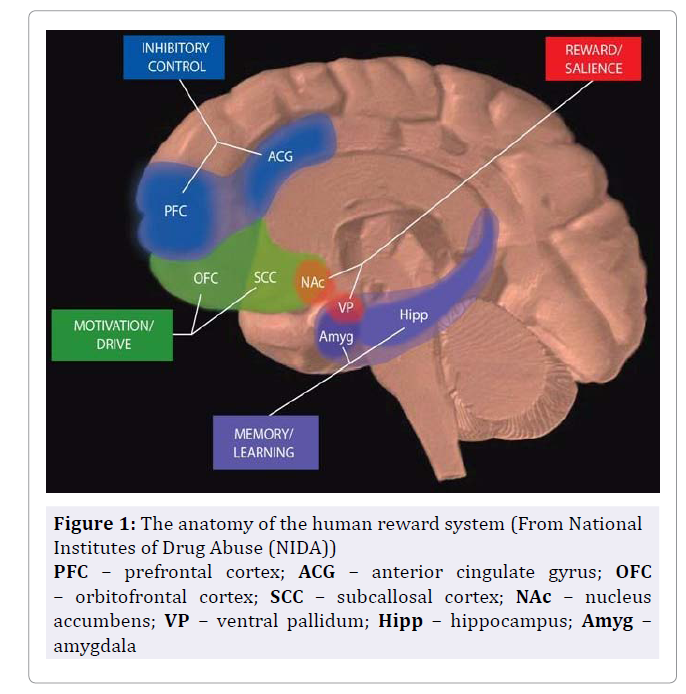
1. Reward/Salience – The Reward/Salience circuit in addiction includes the nucleus accumbens(NAc) and ventral palladium(VP) and associates salience (i.e. importance) with some sort of stimulus behavior (e.g. an addictive drug, a piece of candy, or a cookie). The level of salience attached to this stimulus determines it’s ability to grab attention and elicit a response (e.g. taking the drug or eating the candy or food)
2. Memory/Learning – The Memory/Learning circuit in addiction includes the amygdala(Amyg) and hippocampus(Hipp) and is reinforced by the reward/salience circuit. This circuit participates in forming memories linked to drug use or natural reward. In this circuit, experiences that people have during drug use (environments, objects, people) may prompt memories of drug use and craving for the drug when encountered again.²
3. Motivation/Drive – The Motivation/Drive circuit in addiction includes the orbitofrontal cortex(OFC) and subcallosal cortex(SCC) and is influenced by both the reward/salience circuit and the memory learning circuit. Drug cues and memories of drug use activate the orbitofrontal cortex and cause craving.¹
4. Inhibitory Control / Executive Function – The Inhibitory Control/Executive Function circuit involves the prefrontal cortex(PFC) and anterior cingulate gyrus(ACG). These areas are our higher thought and are what make us human. This circuit allows conscious control of behaviors such as resisting drug-taking or resisting overeating.²
Why is Understanding the Brain Circuitry Important?
The concept of addiction as involving multiple brain circuits is important when considering therapy. The treatment of addiction can’t be undertaken by just one modality (e.g. just a drug for withdrawal, just a drug for cravings, just counseling, etc.). We must employ multiple treatment modalities that consider the brain circuitry involved in addiction if we are to successfully treat addiction and get to the root cause of where and how the addiction started.
What are the Most Important Factors When Considering Treatment?
The 5 most important treatment modalities involved in treating addiction are:
1. Counseling – Addiction Counseling uncovers the emotional reasons the drug was being used and focuses on weakening cue-induced craving with behavioral therapy. This is where true healing occurs, but this is also the deepest layer to uncover in treatment and often can’t be treated appropriately if the other treatment areas aren’t properly addressed first.
2. Medication Assisted Treatment (MAT) – MAT for addiction means using a pharmacologic treatment that blocks the rewarding value of the addictive drug and/or negative effects of withdrawal.
3. Nutritional Support – Locating deficiencies in the addicted individual’s diet and genetic make-up and providing personalized nutritional therapy to help each body deal with the stress of life and the stress of addiction specific to the individual. Providing nutritional support ensures you have enough vitamins and cofactors to run all of your biological systems properly as addiction tends to steal certain nutrients down inflammatory and detoxification pathways, stealing them from the normal everyday processes in your body.
4. Lifestyle Modifications – Addiction stems from and creates disruptive behaviors. Lifestyle modification focuses on changing lifestyle behaviors that perpetuate addiction and weaken the ability say no. This includes smoking cessation, practices for reducing stress, exercise guidance, optimizing sleep habits, and suggesting methods that help in making better choices
5. Spirituality – helps you identify your place, purpose, and calling in life.
1. Volkow N. D., Wang G. J., Fowler J. S., Telang F. (2008). Overlapping neuronal circuits in addiction and obesity: evidence of systems pathology. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 363 3191–3200. 10.1098/rstb.2008.0107
2. Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang G. The addicted human brain: Insights from imaging studies. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2003;111:1444–1451
